Recurrent Sinus Infections
Sinus Infections
Sinus infection, commonly known as sinusitis, is a cold-like condition in which the sinuses are inflamed or swollen. Four or more sinus infections in a year is typically termed "recurrent sinus infections." The paranasal (“around the nose”) sinuses are the void spaces present in the bones that are located around our nose, in the bones of cheeks, behind the eyebrows and forehead and behind the nose in front of the brain. There are some channels that connect these void spaces to the nose. Due to infections, the sinus lining get swollen and block the intermediate channels. And Sinusitis is the condition in which these channels get blocked.

Causes of Sinusitis
There are several causes of sinus infections. The Common Cold virus can cause swelling that contributes to sinusitis. If someone has a Cold for more than seven to ten days, then there is a higher chance that bacterial sinusitis is present. Bacterial infection is a major cause of sinusitis; rarely, fungal infection can also cause sinusitis.
The person’s anatomy can also contribute to the development of sinusitis, including:
- Narrow bony openings in the sinuses
- Nasal polyps
- Deviated nasal septum
- Extra “air cells” in the sinuses (some names include concha bullosa cells, Haller cells, Onodi cells, and frontal cells)
Symptoms of Sinus Infections
Some common symptoms and signs of sinusitis are:
- Postnasal drip (behind the nose drip into the throat)
- Nasal congestion
- Discoloration of nasal discharge
- Altered smell or taste
- Coughing
- Redness and swelling nasal lining
Symptoms from sinus infections and allergies can be confusing. Allergies of the nose tend to cause “rhinitis” (swelling of the passages of the nose only) and include more sneezing, itchiness, and watery nose/eyes. Asthma is another term that is linked with chronic sinus disease. These two conditions can worsen each other, so it important to maximally treat both.
Diagnosis of Sinus Infections
The diagnosis for a sinus infection involves the examination of nose, sinuses and throat. An endoscopy (a tube with a small camera on the end of it is gently inserted into the nose) can helpful to locate the sinus infection and determine if the person has anatomy that worsens their risk for sinus infections. If a sinus infections is severe or lasts for an extended period, a CT scan (picture) of the sinuses may be recommended. These tests will enable the doctor to know the type of infection and which relative medicine should be given to the patient. For example, if the sinusitis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics will be recommended. If nasal polyps are present, your doctor may recommend an anti-inflammatory medicine, such as corticosteroids.
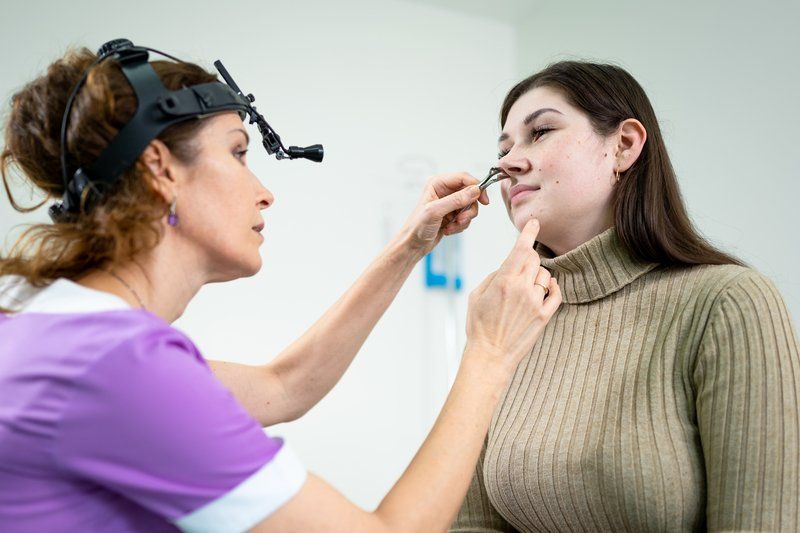
Sinusitis Treatment
Nasal polyps are not the only lumps that can be found in the nose and sinuses. Some lesions can masquerade as nasal polyps.
Surgery - Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery or Balloon Sinus Dilation
If none of the above given treatments work, then surgery is recommended to assistant the medicine to work better. This surgery is performed by an otolaryngologist to open the sinus cavities and allow function drainage of the sinus cavities. An in-office minimally invasive procedure, called balloon sinuplasty or balloon sinus dilation, is also an option without the need for cutting. Other procedures are also considered, including Septoplasty and Inferior Turbinate Surgery.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are recommended for bacterial sinusitis. Overuse of antibiotics can cause resistant bacteria, so antibiotics should be avoided for allergies and viral Colds. The period of medication can vary from 5-28 days, depending on the antibiotic and type of sinusitis. Extended treatments are occasionally recommended. Rarely, resistant sinusitis may require intravenous (IV) courses or direct application of antibiotics into the nose (via irrigations, sprays, or nebulizers).
Antihistamines
Antihistamines help to prevent the allergic reactions and block inflammation.
Topical Nasal Corticosteroids
These are the sprays that prevent swelling and inflammation in nasal passages.
Oral Corticosteroids
Oral corticosteroids reduce inflammation throughout the whole body, including the sinus cavities. These medications often are given for severe inflammation or nasal polyps.
Our Convenient Locations
Contact Us
Have question about our services and treatments? Reach out to us!
Contact Us
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later
Schedule an Appointment with a Fellow-Trained Sinus Surgeon Today
Dr. Thomas Higgins | Dedication to Sinusitis Relief

Our Convenient Locations
Louisville Old Brownsboro Crossing
9850 Von Allmen Court, STE 104, Louisville, KY 40241
Louisville St. Matthews Springs Medical Complex
6420 Dutchmans Parkway STE 380 Louisville, KY 40205
Jeffersonville, Indiana
W Gordon Gutmann Blvd, Jeffersonville, IN 47130 USA
Dr. Thomas S. Higgins
- Rhinology, Sinus & Skull Base, Kentuckiana Ear, Nose & Throat
- Locations in Louisville, Kentucky and Southern Indiana
- Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Communicative Disorders
University of Louisville School of Medicine
Copyright © 2012-2025. Higgins Sinus. All Rights Reserved.
Note: The information contained in these pages is for educational purposes only. It should not be construed as individualized diagnostic and treatment advice. Please see our Privacy Policy as well as our Terms and Conditions. While we will never intentionally share any information you provide us via this website, this contact form and email system is not secure under HIPAA guidelines. Please avoid including personal or medical information you would want to be protected from 3rd party interception. A list of HIPAA identifiers can be found here. Please do not use this form for emergent or urgent matters. Disclosure: We may earn a commission when you use one of our coupons/links to make a purchase.




