Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)

Introduction
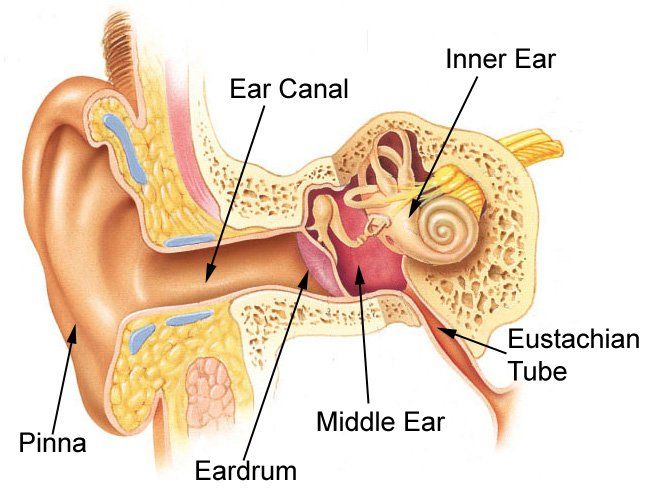
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear and the nasopharynx (back of the nose). The nasopharynx is the area between the upper part of the throat and where the nasal cavity opens at the back. When this tube is functioning normally, it balances the pressure inside the middle ear and that outside of the body. An imbalance in these pressures makes the eardrum to vibrate poorly when sound waves hit it. This leads to a condition called Eustachian tube dysfunction or ETD.
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The main symptom is impaired hearing. Depending on the cause and severity of the condition, the degree of impairment may range from dull, muffled to more serious forms of hearing loss. The symptoms may be in one or both ears. They can be transient, recurrent or long-lasting. Other symptoms include:
- Ear ache
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Dizziness
- Headache may or may not be present
Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Common colds and other infections of the upper respiratory tract are the commonest causes of ETD. Other causes include:
- Blockage of the middle ear by a glue-like substance
- Rhinitis, hay fever and other respiratory tract allergies
- Enlarged adenoids
- Tumors behind the nasal area
- Air travel
Treatment of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
In most cases, this condition will resolve on its own. Other treatment options include:
- Your doctor can teach you how to perform a technique called Valsalva maneuver.
- Use of nasal decongestants (only temporary relief)
- Antihistamine medications
- Corticosteroids nasal sprays for refractory conditions
- Referral to an ear, nose and throat specialist for un-responding or poorly responding conditions. Now there are more treatments available, including Eustachian Tube Dilation.
Although Eustachian tube dysfunction is not life-threatening some of its causes such as post-nasal space area tumors can be. Early investigation and treatment for persistent cases can help to prevent serious complications





